Chapter 13
Airways
Learning Objectives
- Define tracheomegaly.
- Name five common causes of tracheobronchomegaly.
- Name five causes of focal or diffuse tracheal narrowing.
- Name four types of bronchiectasis and identify each type on chest computed tomography (CT).
- Name five common causes of bronchiectasis.
- Recognize the typical appearance of cystic fibrosis on chest radiography and CT.
- Name five important things to look for on a chest radiograph when the patient history is "asthma."
- Name three types of pulmonary emphysema and identify each type on chest CT.
- Recognize the findings of α-1-antitrypsin deficiency on a chest radiograph and CT.
- Recognize the findings of Kartagener syndrome on a chest radiograph and CT and name the three major components of the syndrome.
- Define the term giant bulla, differentiate giant bulla from pulmonary emphysema, and state the role of imaging in patient selection for bullectomy.
- Recognize and describe the significance of a pattern of mosaic lung attenuation on chest CT.
Airway disorders can be categorized into those that
involve the trachea, those that involve the bronchi, and those that
involve the bronchioles, the smallest branching airways leading to
alveoli. Many disorders can, and frequently do, involve more than one
airway compartment. Tracheal disorders will be discussed first, and
disorders involving both the bronchi and bronchioles will be discussed
together. The reader is referred to Chapter 1 for a discussion of normal anatomy of the airways.
Tracheal Disorders
Tracheal shape varies, depending on the phase of the
respiratory cycle. The intrathoracic trachea is round or elliptic on
inspiration images and flat or horseshoe shaped during and at the end
of a forced exhalation as a result of anterior bowing of the posterior
noncartilaginous tracheal membrane during exhalation (1).
Upper limits of normal for coronal and sagittal tracheal dimensions,
respectively, as determined by chest radiographs, are 25 mm and 27 mm
for men and 21 mm and 23 mm for women. The lower limit of normal for
both dimensions is 13 mm in men and 10 mm in women (2).
Mean measurements on computed tomography (CT) of anteroposterior (AP)
and transverse diameters of the extrathoracic trachea, respectively,
are 20.1 mm and 18.4 mm (3); these can increase by as much as 15% in men with aging (4).
CT is superior to chest radiography for detection of
abnormalities of the trachea and main bronchi; sensitivities in
detecting disease on chest radiographs and CT are 66% and 97%,
respectively (5). Spiral multidetector CT,
which allows for the acquisition of a whole thoracic volume during a
single breath-hold, eliminating respiratory motion, is the technique of
choice for noninvasive imaging of the airways. Volume acquisition with
multidetector CT has fostered a renewed interest in two-dimensional and
three-dimensional (3D) reconstructions applied to the tracheobronchial
tree. Potential clinical applications of 3D reconstructions, such as
shaded surface display and volume rendering, include assisting with
diagnoses, replacing bronchoscopy in some instances, and helping in
surgical planning and endobronchial treatments (6).
In the case of a lesion that completely obstructs an airway, CT allows
visualization of the airway beyond the obstruction. However, CT's
virtual bronchoscopy is currently unable to show mucosal detail, and 3D
postprocessing methods are time consuming to perform and rarely
performed in routine clinical practice.
Patients with tracheal disease can be asymptomatic or
may present with cough, dyspnea, wheezing, or stridor. Because of the
variety of conditions that can cause wheezing, a misdiagnosis of asthma
is common (7). Tracheal disorders are generally
organized into those that cause tracheal widening and those that cause
narrowing. CT can demonstrate the degree of widening or narrowing, in
addition to the location and extent of tracheal abnormality; it can
also demonstrate the presence of associated extraluminal disease,
postobstructive atelectasis, and pneumonia. Magnetic resonance imaging
(MRI) is a valuable method for observing the trachea because of its
multiplanar demonstration of the airway, the mediastinal vessels, and
the other structures simultaneously, without the need for contrast
medium or exposing the patient to radiation. MRI is particularly useful
in children and in patients with either vascular rings or tracheal
compression by the innominate artery.
Disorders That Cause Tracheal Widening
Congenital or nonacquired diffuse tracheal widening is
much less common than tracheal narrowing and has a more limited
differential diagnosis. The Mounier-Kuhn syndrome, which affects
primarily men in the fourth and fifth decades, accounts for almost all
cases of nonacquired tracheal widening (8). Thought to be congenital (9),
it is an abnormality of the trachea and main bronchi characterized by
atrophy or absence of elastic fibers and thinning of muscle, which
allows the trachea and main bronchi to become flaccid and markedly
dilated on inspiration, with narrowing or collapse on expiration or
cough. The abnormal airway dynamics and pooling of secretions in broad
outpouchings, or diverticula, of redundant musculomembranous tissue
between the cartilaginous rings predispose patients to the
development of chronic pulmonary suppuration, bronchiectasis, emphysema, and pulmonary fibrosis (10). The trachea is involved from the subglottic region to the carina. A tracheal diameter greater than 3 cm is required for diagnosis, and tracheal widths up to 5.5 cm have been recorded (8). The radiographic and CT features of the condition include marked dilatation of the trachea and mainstem bronchi, tracheal diverticulosis, and a variable incidence of bronchiectasis and chronic pulmonary parenchymal disease (11,12).
P.216
development of chronic pulmonary suppuration, bronchiectasis, emphysema, and pulmonary fibrosis (10). The trachea is involved from the subglottic region to the carina. A tracheal diameter greater than 3 cm is required for diagnosis, and tracheal widths up to 5.5 cm have been recorded (8). The radiographic and CT features of the condition include marked dilatation of the trachea and mainstem bronchi, tracheal diverticulosis, and a variable incidence of bronchiectasis and chronic pulmonary parenchymal disease (11,12).
TABLE 13-1 DISORDERS THAT CAUSE TRACHEOBRONCHOMEGALY | |
|---|---|
|
Several conditions can result in acquired tracheobronchomegaly that may closely resemble that seen in Mounier-Kuhn syndrome (Table 13-1). Some degree of tracheal dilatation may be seen with aging (4,13) and in musicians who play wind instruments (13).
Chronic infection, cigarette smoking, chronic bronchitis, emphysema,
cystic fibrosis (CF), inhalation of noxious fumes, chronic intubation,
and diffuse pulmonary fibrosis can also result in tracheobronchomegaly (10,14,15).
Other conditions associated with tracheal widening, which may in fact
be related to Mounier-Kuhn syndrome, are Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and
cutis laxa (16,17).
Although tracheal narrowing is the usual end result in relapsing
polychondritis - a disorder of cartilaginous inflammation involving the
nose, ear, trachea, and joints - diffuse tracheal widening may develop
occasionally (18). In contrast, nasal and ear
cartilage abnormalities are absent in Mounier-Kuhn syndrome. Additional
causes of secondary tracheobronchomegaly are listed in Table 13-1.
Nevertheless, the majority of cases appear to be sporadic,
predominantly occurring in men in the third and fourth decades of life (9).
Disorders That Cause Tracheal Narrowing
Tracheal narrowing is seen with a variety of disorders and can be idiopathic (7,19,20,21) (Table 13-2).
Strictures of the trachea are usually caused by damage from a cuffed
endotracheal or tracheostomy tube or trauma to the neck (22).
Postintubation tracheal injuries remain the most common indication for
tracheal resection and reconstruction, despite identification of the
causes of these lesions and development of techniques for their
avoidance (23). Tracheomalacia, which is
diagnosed when the trachea collapses more than 50% on expiration, can
also be caused by trauma, and it may be recognized only on dynamic or
expiratory CT scanning (1,24).
TABLE 13-2 DISORDERS THAT CAUSE TRACHEAL NARROWING | |
|---|---|
|
Saber-sheath trachea is diffuse intrathoracic
narrowing of the trachea, with the coronal diameter reaching two thirds
(or less) of the sagittal diameter when measured 1.0 cm above the top
of the aortic arch (25). More than 95% of
patients with this deformity have clinical evidence of chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and saber-sheath trachea is
considered an insensitive but specific sign for COPD on standard chest
radiography (Fig. 13-1) (25,26).
Relapsing polychondritis is a systemic autoimmune
connective tissue disease in which cartilage is affected diffusely by
recurrent episodes of inflammation. The pinnal, nasal, laryngeal, and
tracheal cartilages are most commonly involved. The major airways are
involved in more than 50% of cases, and recurrent pneumonia is the most
common cause of death in these patients (8,27). CT shows diffuse or multifocal fixed narrowing of the tracheobronchial lumen, with associated thickening of the wall (28,29). Dense calcium deposits may be seen in the thickened tracheal cartilage (30).
Amyloidosis of the respiratory tract, both primary and
secondary, is a rare condition that produces focal or diffuse irregular
narrowing of the airway by submucosal deposits of amyloid (22).
Both radiography and CT of the chest can demonstrate diffuse narrowing
or show nodular protrusions into the tracheal lumen that can be
calcified (Fig. 13-2) (8).
Tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica is a benign
condition characterized by multiple submucosal osteocartilaginous
growths along the inner anterolateral surfaces of the trachea (31,32).
Although the etiology is unknown, theories have linked this disorder to
chronic inflammation, degenerative processes, amyloidosis, and
neoplasia (33,34,35).
Radiography and CT of the chest show multiple sessile nodular tumors,
with or without calcification, extending over a long segment of the
trachea and into the main bronchi. In contrast, the nodules in
amyloidosis may be circumferential and can be distinguished from those
of tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica, in which there is always
sparing of the posterior membranous wall.
P.217
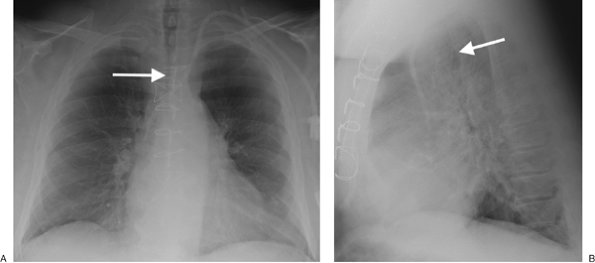 |
FIGURE 13-1. Saber-sheath trachea. A:
Posteroanterior (PA) chest radiograph of a 67-year-old man with
emphysema shows narrowing of the coronal diameter of the trachea (arrow). B: On the lateral view, the tracheal diameter (arrow) is normal or slightly enlarged. |
Wegener granulomatosis is characterized by granulomatous
vasculitis of the upper and lower respiratory tract, usually in
conjunction with renal and other organ involvement. The CT appearance
of airway involvement includes circumferential narrowing of the airway
lumen, abnormal soft tissue within the tracheal rings, and dense
irregular calcification of the tracheal cartilages (36).
Sarcoidosis is another granulomatous disorder that may rarely involve
the trachea and bronchi. Granulomatous sarcoid lesions may exist
intrinsically in the airway, or enlarged hilar nodes may compress the
bronchi extrinsically (37,38).
Many viral, bacterial, or fungal diseases can involve
the trachea. In North America, most cases of laryngotracheobronchitis
are viral in nature; subglottic or laryngeal narrowing is
common, but radiographically demonstrable tracheal narrowing is unusual (7).
P.218
common, but radiographically demonstrable tracheal narrowing is unusual (7).
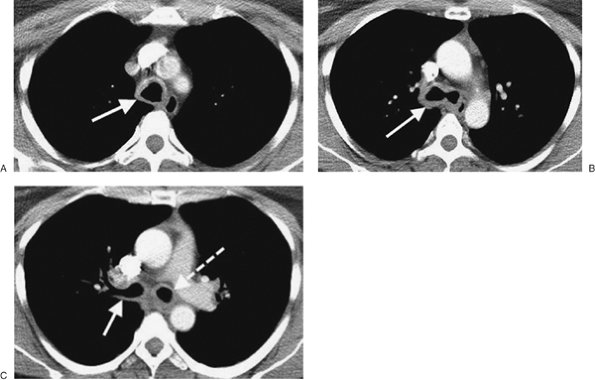 |
FIGURE 13-2. Tracheobronchial amyloidosis. A:
CT of a 44-year-old woman with dysphagia and dyspnea on exertion shows
circumferential thickening and calcification of the tracheal wall (arrow). B: CT at a more inferior level shows thickening of the walls of the main bronchi (arrow). C: CT at a level inferior to (B) shows thickening of the wall of the right upper lobe bronchus (solid arrow) and left main bronchus (dashed arrow). |
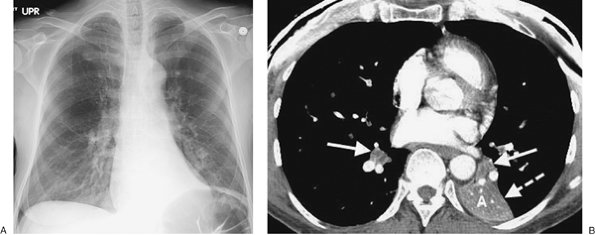 |
FIGURE 13-3. Mucous plugging. A:
PA chest radiograph of a 45-year-old woman with shortness of breath
after cervical spine fusion shows abnormal opacities in both lower
lobes and volume loss in the left lower lobe. B: CT shows low-attenuation material in both lower lobe segmental bronchi (solid arrows), postobstructive atelectasis of the left lower lobe (A), and posteromedial displacement of the left major fissure (dashed arrow). |
Tracheobronchial Filling Defects
In adults, tracheobronchial filling defects are usually produced by mucus (Fig. 13-3) or neoplasms (Figs. 13-4, 13-5, 13-6, 13-7). Less common causes include papilloma, infections (Fig. 13-8), foreign bodies (Fig. 13-9), broncholiths (Fig. 13-10),
and other miscellaneous disorders. If mucus is suspected on a CT scan,
it can be helpful to selectively repeat the scan at the region of
interest after the patient has coughed.
Tracheoesophageal Fistulas
Tracheoesophageal fistulas in adults are almost
exclusively acquired lesions. They occur as a complication of
intrathoracic malignancies (accounting for 60% of cases), infection,
and
trauma (39,40). The diagnosis is usually made with a fluoroscopic contrast study but can be made, in some cases, with CT. In addition to demonstrating the site of a fistula, CT can suggest the etiology and detect pulmonary and mediastinal complications (41).
P.219
P.220
P.221
trauma (39,40). The diagnosis is usually made with a fluoroscopic contrast study but can be made, in some cases, with CT. In addition to demonstrating the site of a fistula, CT can suggest the etiology and detect pulmonary and mediastinal complications (41).
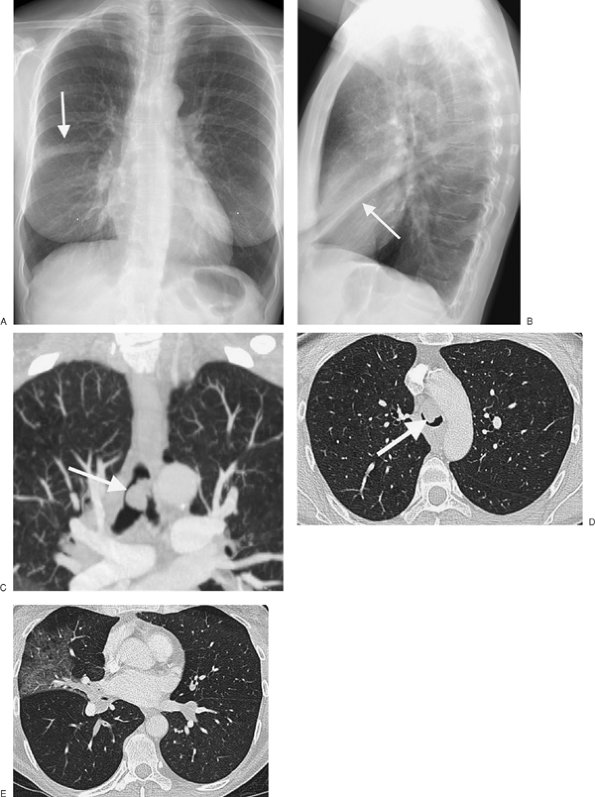 |
FIGURE 13-4. Tracheal adenoid cystic carcinoma. A:
PA chest radiograph of a 59-year-old man with recurrent right middle
lobe pneumonia and cough shows a linear band of opacity in the right
middle lung (arrow). B: Lateral view shows an oblique band of opacity paralleling the inferior aspect of the major fissure (arrow). (Continued ) C: Coronal reformatted CT shows a lobular soft tissue mass (arrow) almost completely obstructing the lumen of the trachea just above the level of the carina. D: Axial CT shows that the mass (arrow) almost completely fills the lumen of the trachea. E: CT at the level of the inferior pulmonary veins shows postobstructive atelectasis and pneumonia in the right middle lobe. |
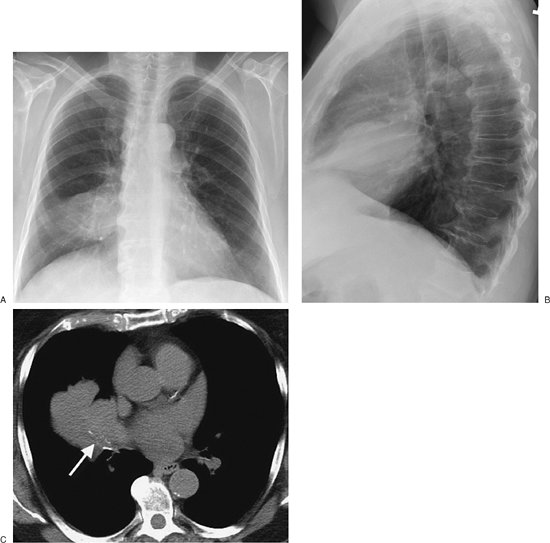 |
FIGURE 13-5. Metastatic endometrial carcinoma. A: PA chest radiograph of a 75-year-old woman shows a mass adjacent to the right hilum. B:
Lateral view shows the mass projected over the heart. The contours of
the mass suggest that it is related to the inferior edge of the major
fissure. C: Axial CT shows low-attenuation material obliterating the lumen of the right middle lobe bronchus (arrow).
Note that the bronchial wall is outlined by calcium. Tumor is growing
through the bronchus into the right middle lobe. The opacity seen on
the chest radiograph represents tumor and collapsed right middle lobe. |
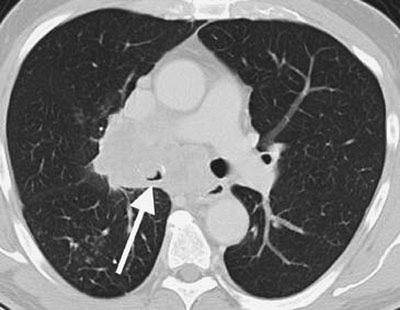 |
FIGURE 13-6. Endobronchial non–small cell carcinoma.
CT of a 63-year-old woman with cough shows a soft tissue mass that
almost completely obliterates the lumen of the bronchus intermedius (arrow). |
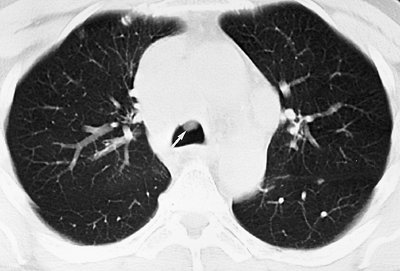 |
FIGURE 13-7. Tracheal metastasis. CT of a 64-year-old woman with renal cell carcinoma shows a soft tissue mass adjacent to the anterior wall of the trachea (arrow)
representing one of many biopsy-proven metastases to the trachea. Mucus
could have a similar appearance, but it will usually clear with a
repeated scan after the patient clears the throat. |
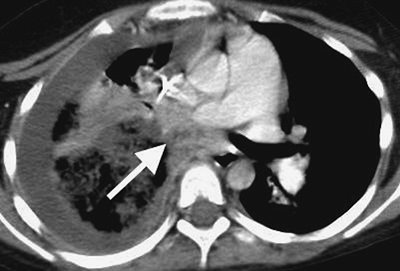 |
FIGURE 13-8. Endobronchial blood clot. CT of a 10-year-old girl with leukemia and Rhizopus necrotizing pneumonia shows a filling defect occluding the bronchus intermedius (arrow).
The right middle and lower lobes were surgically resected; pathology
showed pulmonary artery and vein thromboses, diffuse pneumonia and
pulmonary hemorrhage, and clotted blood in the bronchus intermedius. |
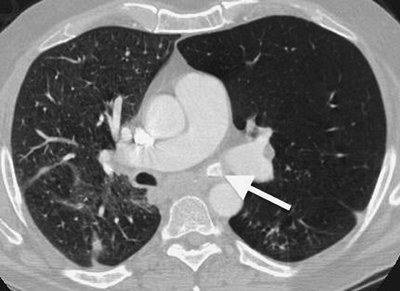 |
FIGURE 13-9. Endobronchial foreign body. CT shows a radiopaque foreign body (arrow)
in the left main bronchus. Note the hyperlucency and hyperinflation of
the left upper and lower lobes secondary to air trapping. A chicken
bone was removed from the airway. |
Congenital Tracheobronchial Anomalies
Congenital tracheobronchial anomalies can present as
life-threatening emergencies at birth, or they may go undiagnosed for
years. Clinical symptoms are often nonspecific, and radiographic
evaluation is frequently required to localize and characterize the
lesion before endoscopy, surgery, or medical management. The
radiologist must be on the alert for unsuspected additional associated
anomalies involving airways, lungs, great vessels, and the esophagus,
which occur with relative frequency.
Tracheal webs produce localized areas of narrowing with
no associated deformity of the underlying cartilage. The thickness of
the webs determines the severity of obstruction and the therapeutic
approach (42). Congenital tracheal stenosis may
occur in any portion of the trachea, usually involving more length and
depth of the trachea than webs, and is more likely to require resection
rather than dilatation alone. Stenosis secondary to long-term
compression by a dilated esophagus, abnormal great vessels, or
cervicomediastinal masses results in a focal fibrous and cartilaginous
deformity that persists for some time after the mass is removed.
Congenital tracheal stenosis is frequently associated with bronchial
stenosis; pulmonary hypoplasia or agenesis; tracheal bronchus;
tracheoesophageal fistula; tracheomalacia; anomalies of vertebrae,
ribs, and thumbs; and cardiac anomalies.
Tracheomalacia is an abnormally flaccid trachea that may
involve all or part of the trachea and results in abnormal
anteroposterior tracheal collapse during expiration of ≥50% of
cross-sectional area. The innominate artery compression syndrome can
result in secondary tracheomalacia, in which there is persistent
narrowing of the anterior tracheal wall at the level of the thoracic
inlet. Short trachea, which occurs when there are 15 or fewer tracheal
rings, can be diagnosed on CT when the tracheal bifurcation lies above
the fourth thoracic vertebral body in children younger than 2 years old
or above the fifth thoracic vertebra thereafter (43).
Aberrant tracheal bronchus (so-called "pig bronchus," or
bronchus suis), the most common anomalous airway pattern, is reported
in 2% of children during bronchoscopy examination (44).
It occurs most commonly in boys, arising most often from the right
lateral tracheal wall within 2 cm of the carina. It can be
asymptomatic, or it may result in right upper lobe infection,
atelectasis, or bronchiectasis, usually from a stenotic bronchial
segment and poorly cleared secretions. The CT appearance is that of a
bronchus arising from the trachea in a section more cephalad than the
carina (Fig. 13-11) (45).
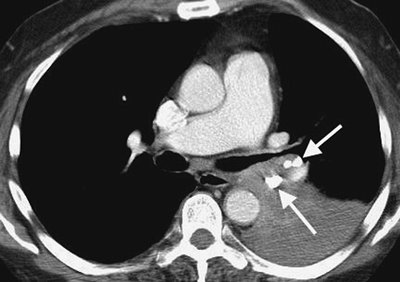 |
FIGURE 13-10. Broncholithiasis.
CT of a 72-year-old man with cough, wheezing, and increasing shortness
of breath shows large calcifications in the left hilum and left lower
lobe bronchus (arrows). Note postobstructive atelectasis of the left lower lobe. |
P.222
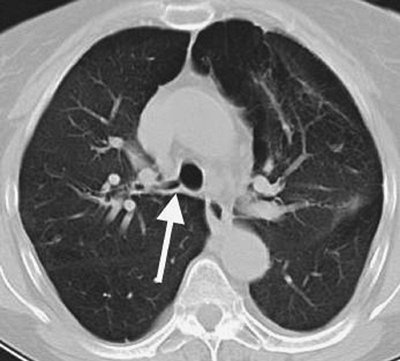 |
FIGURE 13-11. Aberrant tracheal bronchus. CT of a 58-year-old woman with cough and recurrent pneumonia shows a so-called "pig bronchus" (arrow) arising from the right lateral wall of the trachea, above the level of the carina. |
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
COPD refers to a group of disorders characterized by
chronic or recurrent obstruction to airflow. Five principal disorders
fall under this heading (Table 13-3), although
the term is commonly used clinically to refer to emphysema. Because
these disorders are sometimes difficult to distinguish from one another
on chest radiography, the term COPD should not be restricted to emphysema.
Asthma
There is no universally accepted definition of asthma;
it may be regarded as a diffuse, obstructive lung disease with
hyperreactivity of the airways to a variety of stimuli and a high
degree of reversibility of the obstructive process, which may occur
either spontaneously or as a result of treatment. Asthma is a complex
disorder involving biochemical, autonomic, immunologic, infectious,
endocrine, and psychologic factors in varying degrees in different
individuals. Both large and small airways may be involved, again to
varying degrees. The three elements that contribute to airway
obstruction in asthma are: (i) spasm of smooth muscle; (ii) edema and
inflammation of the mucous membranes lining the airways; and (iii)
intraluminal exudation of mucus, inflammatory cells, and cellular
debris. Asthma can be a benign, self-limiting problem; it can lead to
acute respiratory failure; or it can be a chronic, recurrent disease
that leads to debilitating, irreversible airflow obstruction and COPD.
Emphysema is not a prominent finding in the lungs of nonsmoking
patients with asthma, even in those with severe disease (46).
TABLE 13-3 CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE | |
|---|---|
|
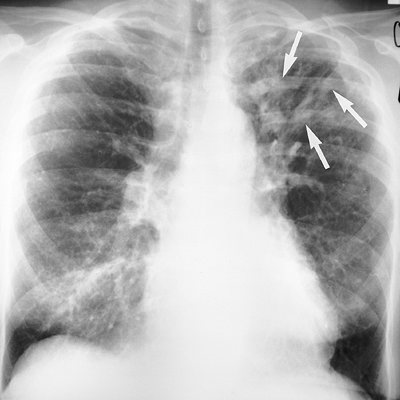 |
FIGURE 13-12. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis.
PA chest radiograph of a 64-year-old woman with a long history of
asthma shows multiple tubular opacities in the left upper lobe (arrows) representing dilated bronchi filled with mucus, debris, and fungal hyphae. |
Chest radiographs of patients with asthma can be normal,
show increased lung markings and hyperinflation, or show low lung
volumes and multifocal atelectasis. CT findings can include
bronchiectasis involving mostly subsegmental and distal bronchi,
bronchial wall thickening, small centrilobular opacities, and decreased
lung attenuation (47). Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) occurs with a greater prevalence in patients with asthma and CF (48) (Figs. 13-12 and 13-13). Central bronchiectasis on CT is the hallmark of ABPA.
Bronchial wall thickening in asthma (which is assessed subjectively on CT) may reflect bronchial and peribronchial inflammation as well as increased smooth muscle, mucous gland, cartilage, and submucosal area (49,50). Areas of hyperlucency are caused by decreased lung perfusion secondary to reflex vasoconstriction in hypoventilated areas, and by air trapping (51) (Fig. 13-14). Emphysema seen on the CT scans of patients with asthma is attributed to cigarette smoking (52). Small centrilobular opacities may correspond to plugging or to thickening of the bronchiole walls (49). Because central airway lesions and mitral stenosis can produce symptoms attributed to asthma, the airways, cardiac silhouette, and pulmonary vasculature should always be evaluated closely on every chest radiograph when the clinical history is "asthma." The chest radiograph should also be assessed for evidence of pneumonia, which is known to exacerbate asthma, and pneumomediastinum (Fig. 13-15) and pneumothorax, as evidence of alveolar rupture that can be caused by wheezing and coughing (Table 13-4).
P.223
Bronchial wall thickening in asthma (which is assessed subjectively on CT) may reflect bronchial and peribronchial inflammation as well as increased smooth muscle, mucous gland, cartilage, and submucosal area (49,50). Areas of hyperlucency are caused by decreased lung perfusion secondary to reflex vasoconstriction in hypoventilated areas, and by air trapping (51) (Fig. 13-14). Emphysema seen on the CT scans of patients with asthma is attributed to cigarette smoking (52). Small centrilobular opacities may correspond to plugging or to thickening of the bronchiole walls (49). Because central airway lesions and mitral stenosis can produce symptoms attributed to asthma, the airways, cardiac silhouette, and pulmonary vasculature should always be evaluated closely on every chest radiograph when the clinical history is "asthma." The chest radiograph should also be assessed for evidence of pneumonia, which is known to exacerbate asthma, and pneumomediastinum (Fig. 13-15) and pneumothorax, as evidence of alveolar rupture that can be caused by wheezing and coughing (Table 13-4).
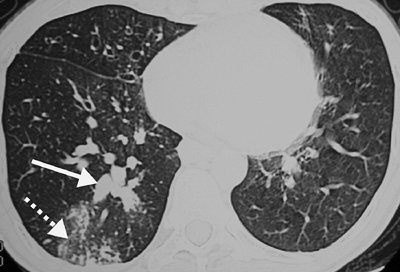 |
FIGURE 13-13. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. CT shows central bronchial dilatation and impaction (solid arrow). Peripheral nodular and ground-glass opacities (dashed arrow) represent impaction of small airways and peribronchiolar inflammation. |
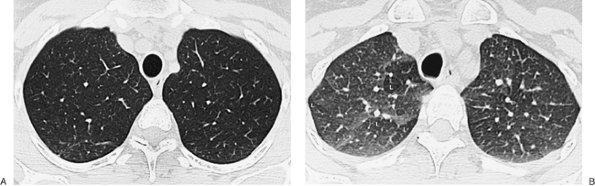 |
FIGURE 13-14. Asthma. A: Inspiratory CT of a 34-year-old woman with steroid-dependent asthma is normal. Note the round contour of the trachea. B: Expiratory image at the same level as (A) shows areas of lucency (L), representing air trapping. Note the flattened posterior tracheal contour on expiration. |
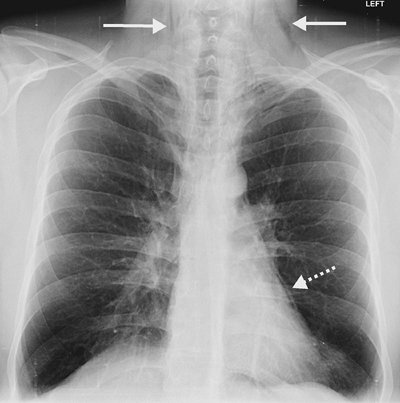 |
FIGURE 13-15. Pneumomediastinum. PA chest radiograph of a patient with asthma shows mediastinal air outlining the heart (dashed arrow) and extending into the neck bilaterally (solid arrows). |
Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis, defined as irreversible dilatation of
the bronchial tree, can cause chronic sputum production and hemoptysis,
and it can be described morphologically as cylindric, varicose, cystic, or traction in type (53). Cylindric bronchiectasis, the mildest form, is characterized by smooth, uniformly dilated bronchi (Figs. 13-16 and 13-17).
Sectioned lengthwise, these bronchi resemble nontapering "tram tracks";
sectioned crosswise, the bronchi appear round or oval. Beaded
dilatation of bronchi describes the varicose type (Fig. 13-18); cystic bronchiectasis, the most severe type, is characterized by cysts in clusters, often with air–fluid levels (Figs. 13-19 and 13-20).
Traction bronchiectasis refers to irreversible dilatation of bronchi
and bronchioles in areas of pulmonary fibrosis. It occurs predominantly
in the peripheral portions of lung, where bronchi contain less
supporting cartilage (see Fig. 3-3B) (54). There are numerous causes of bronchiectasis; these can be remembered with the mnemonic "BRONCHIECTASIS" (Table 13-5).
Although patients with bronchiectasis rarely have a normal chest radiograph (55), the chest radiographic findings are neither sufficiently sensitive nor specific enough to be of value
in the accurate assessment of bronchiectasis, and they are unreliable in determining the severity and extent of the disease (55,56,57). The common radiographic findings are loss of definition and increase in number and size of the bronchovascular markings (caused by peribronchial inflammation/fibrosis and the presence of retained secretions), tram tracking, tubular or ring-shaped opacities with central lucency if the airways are air filled, central opacity if there is mucoid impaction, and cystic spaces that can be up to 2 cm in diameter.
P.224
in the accurate assessment of bronchiectasis, and they are unreliable in determining the severity and extent of the disease (55,56,57). The common radiographic findings are loss of definition and increase in number and size of the bronchovascular markings (caused by peribronchial inflammation/fibrosis and the presence of retained secretions), tram tracking, tubular or ring-shaped opacities with central lucency if the airways are air filled, central opacity if there is mucoid impaction, and cystic spaces that can be up to 2 cm in diameter.
TABLE 13-4 THINGS TO LOOK FOR ON THE CHEST RADIOGRAPH WHEN THE PATIENT HISTORY IS "ASTHMA" | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Early studies assessing the accuracy of conventional CT
in diagnosing bronchiectasis resulted in sensitivities of 60% to 80%
and specificities of 86% to 100% (57,58,59,60).
With the use of 1.5-mm collimation at 10-mm intervals, sensitivity with
CT improved to a range of 96% to 98%, with specificity of 93% to 99% (61,62).
Thin-section CT is now the accepted gold standard for diagnosing
bronchiectasis. With current state-of-the-art multidetector CT, routine
imaging of the lungs with 3-mm collimation and 1.25-mm reformatting
will allow for diagnosis of most cases of bronchiectasis, even very
mild cases. The most reliable finding for the diagnosis of cylindric
bronchiectasis is visualization of bronchi within 1 cm of costal or
paravertebral pleura, or visualization of bronchi abutting the
mediastinal pleura. Although lack of normal bronchial tapering and
increased bronchoarterial ratios are helpful in the diagnosis of
bronchiectasis, these findings can also be seen in 10% to 20% of healthy subjects.
P.225
bronchiectasis, these findings can also be seen in 10% to 20% of healthy subjects.
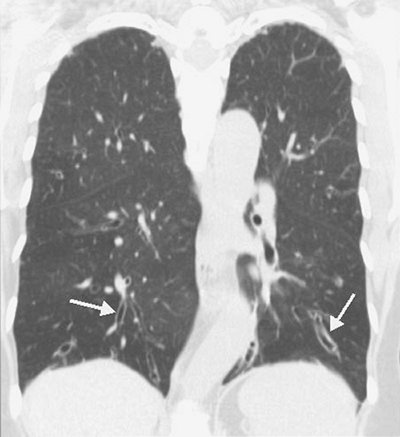 |
FIGURE 13-16. Cylindric bronchiectasis. Coronal reformatted CT shows smooth, uniformly dilated bronchi (arrows), predominantly in the lower lungs. |
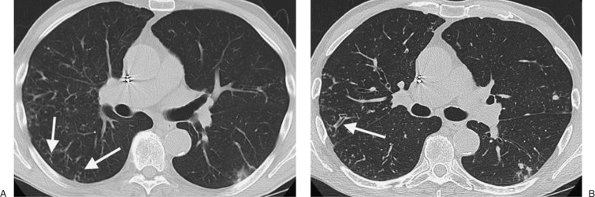 |
FIGURE 13-17. Atypical mycobacterial bronchiolitis. A: CT shows tree-in-bud opacities in the periphery of the right lower lobe (arrows). B: Thin-section CT (1.25 mm) shows cylindric bronchiolectasis in the right lower lobe (arrow). Note bronchiolar opacities in the left lower lobe as well. |
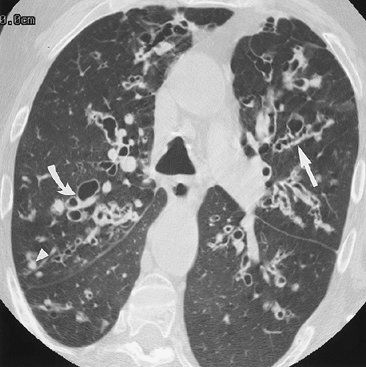 |
FIGURE 13-18. Varicose and cystic bronchiectasis.
CT of a 66-year-old man shows dilated bronchi and bronchioles. In
profile, some of the bronchiectatic airways have the "beaded"
appearance of varicose bronchiectasis (straight arrow); in cross section, some are grouped together like a "cluster of grapes," as is seen with cystic bronchiectasis (curved arrow).
The bronchial and bronchiolar walls are thickened. Some of the dilated
bronchioles are filled with mucus, forming peripheral nodular opacities
(arrowhead). |
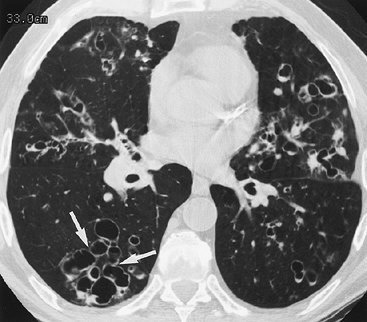 |
FIGURE 13-19. Cystic bronchiectasis. CT of a 65-year-old woman with a history of Pasteurella multocida infection of the lungs shows dilated bronchi and bronchioles, forming a "cluster of grapes" in the right lower lobe (arrows). |
Despite the ease with which bronchiectasis can be identified on CT in most cases, there are a number of potential pitfalls (63).
These include artifacts from both respiratory and cardiac motion, and
inappropriate collimation and electronic windowing. A number of diffuse
lung diseases can simulate bronchiectasis, especially cystic
bronchiectasis; these include Langerhan cell histiocytosis,
lymphangioleiomyomatosis, cystic changes related to connective tissue
diseases or lymphocytic interstitial pneumonitis or in patients with
acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and Pneumocystis jiroveci
pneumonia, emphysema, and cystic metastases. The characteristic
combination of "cyst" paired with the accompanying pulmonary artery is
sometimes helpful in confirming bronchiectasis, as is variation in the
sizes of bronchiectatic "cysts" with inspiration and expiration, a
feature that is not usually seen with other types of cystic lesions.
Following cystlike lesions from one CT scan section to another and
noting their relationship to central airways and their "tubular" nature
also allow for accurate distinction between bronchiectasis and other
cystic diseases, in most cases. This can be facilitated by
reconstructing multidetector CT data to create
maximum-intensity-projection images and coronal reformations.
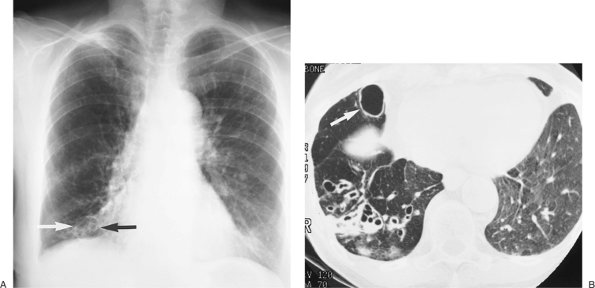 |
FIGURE 13-20. Cystic bronchiectasis. A:
PA chest radiograph of a 78-year-old woman shows increased
"interstitial markings" in the lower lungs. There is a prominent
thin-walled "ring shadow" in the right middle lobe (arrows). B:
CT shows thick-walled, dilated bronchioles forming a “cluster of
grapes” in the right lower lobe and a large dilated airway in the right
middle lobe (arrow). Patchy areas of dense airspace opacity in the right lower lobe were thought to represent acute pneumonia. |
TABLE 13-5 CAUSES OF BRONCHIECTASIS | |
|---|---|
|
P.226
The dyskinetic cilia syndrome, first described in 1976 (64),
represents a spectrum of genetically determined defects in ciliary
structure and function that interfere with mucociliary clearance.
Although the term immotile cilia syndrome
has been used, in many cases the cilia demonstrate some motility
(although dyskinetic). Described conditions include (a) situs inversus,
paranasal sinusitis, and bronchiectasis (the three major components of
Kartagener syndrome) (Figs. 13-21 and 13-22); (b) recurrent upper and lower respiratory tract infections; (c) and immotile sperm and infertility.
Cystic Fibrosis
CF is a relatively common genetic disorder that affects
the upper and lower respiratory tracts, pancreas, liver and
gallbladder, intestines, and genital tract. Approximately one in 1,600
live births is affected by this autosomal recessive disease, which
occurs predominantly in Caucasians. In 1985, the CF defect was
determined to be located on chromosome 7 (65), and 4 years later the CF gene was identified by positional cloning (66,67,68). This new knowledge gave rise to new therapies, including in vivo gene therapy (69). The median survival age rose from about 18 years in 1976 to 29 years in the early 1990s (70,71).
Chest radiographic findings in adult patients with CF include hyperinflation and atelectasis as well as bronchiectasis (72). CT shows the presence, severity, and extent of bronchiectasis, peribronchial thickening, mucous plugging (Fig. 13-23), abscesses, bullae, lung collapse, and dense parenchymal opacification (73) (Fig. 13-24). In early stages of the disease, the upper lungs are involved to a greater extent than the lower lungs (Fig. 13-25). As the disease progresses, the process becomes more diffuse and an upper lung–predominant pattern may not be appreciated.
Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis is defined clinically as a chronic or
recurrent increase in the volume of mucoid bronchial secretions
sufficient to cause expectoration, occurring on most days during at
least 3 consecutive months for no less than 2 consecutive years (74).
It is common among cigarette smokers. The diagnosis is based on the
presence of chronic productive cough in the absence of any specific
cause, such as bronchiectasis or chronic infection. The radiographic
features are nonspecific and include tubular shadows, thickened
bronchial walls, hyperinflation of the lungs, and areas of pulmonary
oligemia. The term dirty lung has been
used to describe the increase in bronchovascular markings.
Hyperinflation and oligemia are probably a result of associated
pulmonary emphysema. Findings of centrilobular emphysema can
predominate on CT of patients with chronic bronchitis. Radiographic and
CT features are insensitive and nonspecific, and a high degree of
interobserver variability further limits the diagnostic capabilities of
imaging.
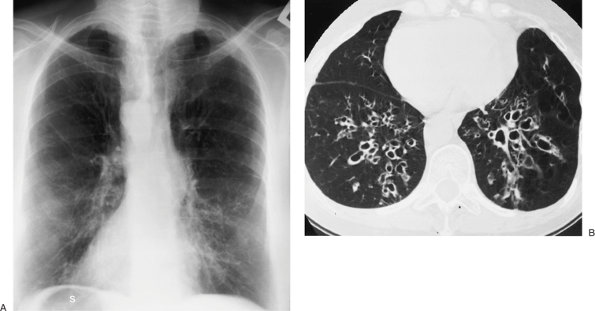 |
FIGURE 13-21. Kartagener syndrome. A: PA chest radiograph of a woman with sinusitis shows dextrocardia, a right-sided stomach bubble (S), and subtle bilateral lower lobe "interstitial" opacities. B: CT shows bilateral lower lobe cystic bronchiectasis. |
Bronchiolitis
Evaluation of the bronchioles, defined as peripheral
airways that do not contain cartilage, requires an understanding of the
anatomy of the secondary pulmonary lobule, the smallest portion of lung
that is surrounded by connective tissue septa. The lobular bronchioles
measure no more than 1 mm in diameter (75), and
their walls are less than 0.1 mm thick. Normal bronchioles are
generally not seen on thin-section CT. However, bronchiolar
abnormalities may be detected when there is thickening of the
bronchiolar wall, peribronchiolar inflammation and fibrosis, and
bronchiolectasis with or without filling of the dilated bronchiole with
secretions (76).
Another CT feature of bronchiolar (small-airway) disease
is a mosaic pattern of lung attenuation, which can also be seen with
pulmonary vascular and infiltrative lung diseases. In cases of small
airway disease, areas of variable lung attenuation that form a mosaic
pattern, which is accentuated during forced exhalation, represent air
trapping, hypoxic vasoconstriction, and mechanical pressure on blood
vessels (77). On CT obtained at end-exhalation,
air trapping is recognized as a lack of increase in attenuation or a
lack of decrease in volume of areas of abnormally lucent lung. In small
airway disease, the size and number of vessels in the abnormally lucent
area of lung are decreased relative to areas of higher-attenuation
lung. Air trapping can
also be seen with pulmonary vascular diseases but not with infiltrative diseases.
P.227
P.228
also be seen with pulmonary vascular diseases but not with infiltrative diseases.
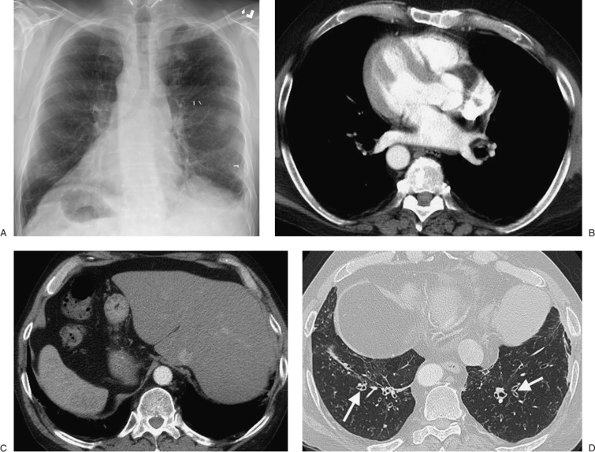 |
FIGURE 13-22. Kartagener syndrome. A: PA chest radiograph of a 56-year-old man shows dextrocardia and a right-sided stomach bubble. B: CT confirms dextrocardia. C: CT at a level inferior to (B) shows situs inversus, with the liver on the left and the spleen on the right. D: CT with lung windowing shows bibasilar bronchiectasis (arrows). |
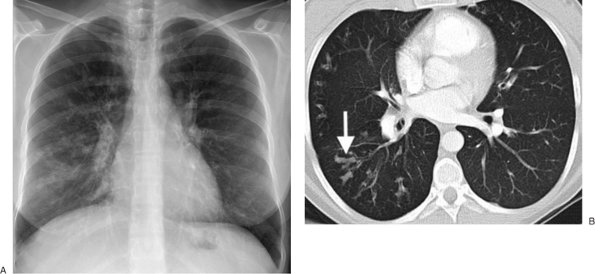 |
FIGURE 13-23. Cystic fibrosis. A:
PA chest radiograph of a 28-year-old woman with cystic fibrosis shows
bilateral bronchiectasis, along with tubular and nodular opacities
representing mucus-impacted airways. B: CT shows mucous plugging of distal airways (arrow). |
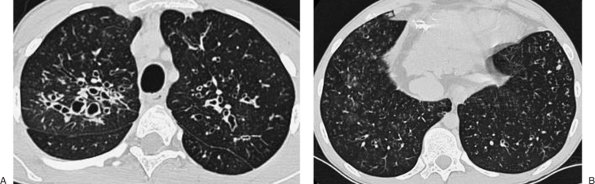 |
FIGURE 13-24. Cystic fibrosis. A: CT of a 22-year-old man with cystic fibrosis shows extensive bronchiectasis and bronchial wall thickening in the upper lobes. B: CT at a more inferior level shows extensive involvement of the small airways. |
Obliterative bronchiolitis (OB) is defined
pathologically as irreversible fibrosis of small-airway walls that
causes the airway lumina to become narrow or obliterated. Constrictive bronchiolitis,
which emphasizes the fibrotic and extrinsic nature of the lesion, is a
synonym for OB and is favored by some authors since it avoids confusion
with bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia, a condition now
more commonly referred to as cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (78). The clinical criteria
used for the diagnosis of OB are irreversible airflow limitation, with a forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) that is less than 60% of the predicted value, in the absence of emphysema, chronic bronchitis, asthma, or other cause of airway obstruction (79). OB and cryptogenic organizing pneumonia are not thought to be related, although they can occur as a result of similar etiologic factors. Both are commonly idiopathic. OB is a common sequela of heart or lung transplantation, representing chronic rejection in lung transplantation, and bone marrow transplantation, where OB represents chronic graft-versus-host disease. OB is a component of Swyer-James syndrome related to childhood viral infection (Fig. 13-26).
P.229
used for the diagnosis of OB are irreversible airflow limitation, with a forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) that is less than 60% of the predicted value, in the absence of emphysema, chronic bronchitis, asthma, or other cause of airway obstruction (79). OB and cryptogenic organizing pneumonia are not thought to be related, although they can occur as a result of similar etiologic factors. Both are commonly idiopathic. OB is a common sequela of heart or lung transplantation, representing chronic rejection in lung transplantation, and bone marrow transplantation, where OB represents chronic graft-versus-host disease. OB is a component of Swyer-James syndrome related to childhood viral infection (Fig. 13-26).
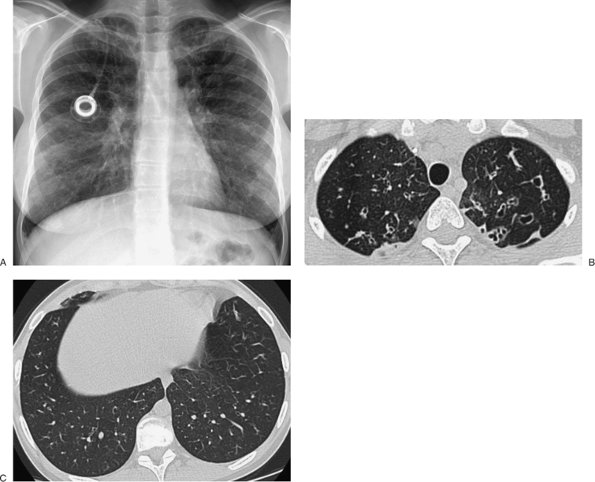 |
FIGURE 13-25. Cystic fibrosis. A:
PA chest radiograph of a 19-year-old man with cystic fibrosis shows
diffuse bilateral bronchiectasis, bronchial wall thickening, and areas
of mucoid impaction. B: CT of the upper lungs confirms the chest radiographic findings. C:
CT at a more inferior level shows normal lung bases. Early in the
course of the disease process, it is typical for the upper lungs to be
more involved than the lower lungs. As the disease progresses, an upper
lung predominance may not be appreciated. |
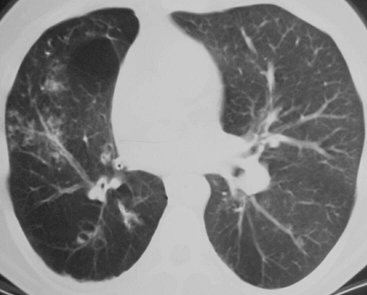 |
FIGURE 13-26. Swyer-James syndrome.
CT shows bronchiectasis, bronchiolectasis, tree-in-bud opacities, and
bullae in the right lung. The right lung is hyperlucent as a result of
air trapping related to obliterative bronchiolitis. The right pulmonary
artery is diminutive, another feature of Swyer-James syndrome. |
Chest radiographs are usually normal in OB but can show
slowly progressive hyperinflation. The CT findings include
bronchiolectasis, centrilobular branching structures and nodules caused
by peribronchiolar thickening and bronchiolectasis with secretions (80), and mosaic lung attenuation (80,81,82,83) (Fig. 13-27).
Interpretation of air trapping must be made with caution, because
occasional isolated areas of lobular air trapping can be seen in
healthy individuals (51).
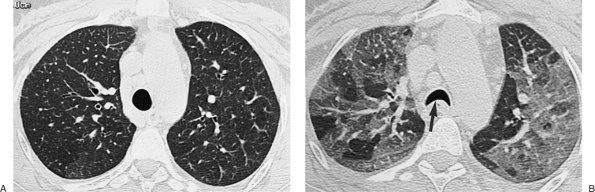 |
FIGURE 13-27. Obliterative bronchiolitis. A: Inspiratory CT of a 40-year-old woman with a transplanted heart is normal. B:
Expiratory CT shows diffuse areas of abnormal parenchymal lucency,
representing air trapping. Note anterior bowing of posterior membranous
trachea on expiration (arrow). |
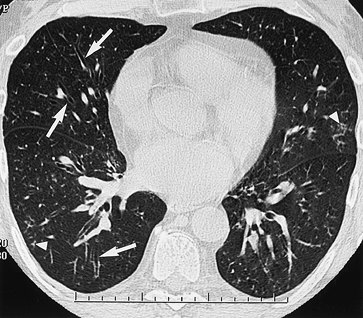 |
FIGURE 13-28. Diffuse panbronchiolitis.
CT of a 61-year-old nonsmoking man with chronic sinusitis, cough,
fever, shortness of breath, scant sputum production, and mixed
restrictive and obstructive pattern on pulmonary function tests shows
cylindric bronchiectasis and bronchiolectasis (arrows), along with peripheral nodular and linear branching opacities representing dilated, impacted bronchioles (arrowheads). |
Pathologic changes occur in the small airways of essentially all smokers (84,85). Respiratory bronchiolitis, also referred to as smoker's bronchiolitis (86,87),
involves the respiratory bronchioles and is characterized by mild
chronic inflammation of the bronchioles associated with accumulation of
pigmented macrophages in respiratory bronchioles and adjacent alveoli.
The condition may be severe enough to produce clinical symptoms of
cough and shortness of breath and to produce CT abnormalities,
including areas of ground-glass attenuation, centrilobular
micronodules, and air trapping (88,89).
The abnormalities usually involve predominantly the upper lungs (a
distribution similar to that of smoking-related centrilobular
emphysema) but may be diffuse.
P.230
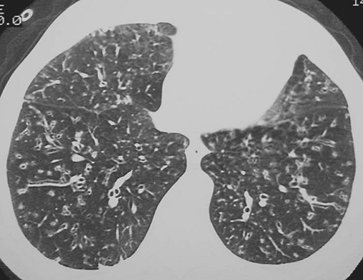 |
FIGURE 13-29. Diffuse panbronchiolitis. CT shows diffuse bronchiectasis, bronchiolectasis, airway wall thickening, and tree-in-bud opacities. |
Diffuse panbronchiolitis is an inflammatory lung disease
of unclear etiology that is prevalent in Asians and rare in Europeans
and North Americans. Histologically, there is thickening of the walls
of respiratory bronchioles and associated peribronchiolitis, and, in
advanced stages, bronchiolectasis (90). The chest radiograph can show disseminated small nodular opacities up to 2 mm in size (91).
The findings on CT have been classified into four types: (a) nodules
alone, (b) nodules associated with branching linear opacities, (c)
nodules with ring-shaped or small tubular opacities (probable
bronchiolectasis), and (d) large cystic opacities accompanied by
dilated proximal bronchi (90,92) (Figs. 13-28 and 13-29).
Bronchopneumonia, regardless of the type of infectious
agent, can result in centrilobular nodules or branching structures on
CT, which are related to peribronchiolar consolidation or pus-filled
small airways (91), and it is the most common cause of the "tree-in-bud" pattern seen on CT (93,94) (Figs. 13-30, 13-31, 13-32, 13-33, 13-34). Aspiration of infected or other material into the small airways is another common cause of the tree-in-bud pattern (Figs. 13-35 and 13-36).
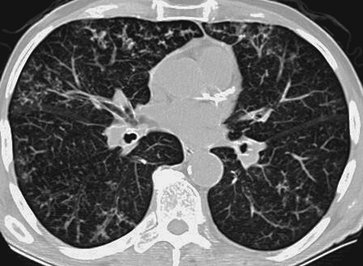 |
FIGURE 13-30. Infectious bronchiolitis.
Maximum-intensity-projection CT of an 81-year-old man with cough and
weight loss shows diffuse bronchiolitis, with prominent tree-in-bud
opacities in the periphery of the lungs. |
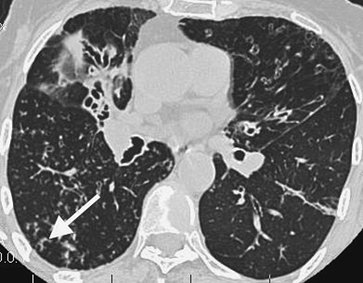 |
FIGURE 13-31. Atypical mycobacterial bronchiolitis.
CT of an 88-year-old woman with chronic cough shows varicose and cystic
bronchiectasis in the right middle lobe and tree-in-bud opacities in
the right lower lobe (arrow). |
Emphysema
Pulmonary emphysema, as defined by the National Heart,
Lung, and Blood Institute, is “an abnormal permanent enlargement of the
airspaces distal to the terminal bronchioles, accompanied by
destruction of the alveolar walls, and without obvious fibrosis” (95).
Three different morphologic subtypes of emphysema have been described
according to their location in the secondary pulmonary lobule: centrilobular, panlobular, and paraseptal (distal lobular) (Table 13-6). A fourth type of emphysema, paracicatricial emphysema, results from and is
always associated with pulmonary fibrosis and therefore does not meet the strict definition of emphysema.
P.231
always associated with pulmonary fibrosis and therefore does not meet the strict definition of emphysema.
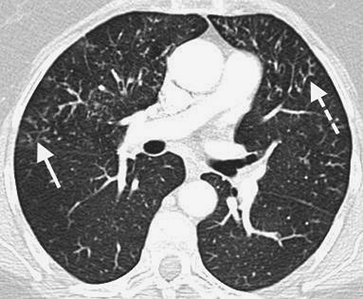 |
FIGURE 13-32. Atypical mycobacterial bronchiolitis. CT of a 69-year-old woman with fever and cough shows tree-in-bud opacities in the right middle lobe (solid arrow) and cylindric bronchiectasis in the lingula (dashed arrow). |
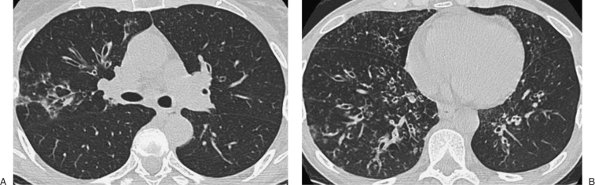 |
FIGURE 13-33. Mycobacterium avium complex infection. A: CT of a 58-year-old woman shows cylindric bronchiectasis in the right middle lobe. B: Extensive bronchiectasis, bronchiolectasis, airway wall thickening, and tree-in-bud opacities are seen in the lower lobes. |
Emphysema is found at autopsy in up to 66% of adult patients (96,97),
but clinical detection of disease during life is difficult unless the
condition is advanced. The presence of airflow obstruction alone is a
sensitive indicator of the presence of emphysema but is not specific,
since asthma, irreversible small-airway disease, and certain forms of
interstitial lung disease may also result in decreased FEV1 (95,98,99).
Evidence of impairment in gas transfer, as assessed with carbon
monoxide diffusing capacity, is more sensitive than abnormal spirometry
for the diagnosis of emphysema; it is also nonspecific, however, and
patients may have up to 30% of their lung involved with emphysema but
have no evidence of functional impairment (100). The accuracy of diagnosis based on findings from chest radiographs depends on the severity of parenchymal destruction (101,102).
CT findings correlate with the presence and severity of morphologic
emphysema better than chest radiographic findings or results of
pulmonary function tests (103,104),
although several studies that assessed CT with 10-mm and 1-mm
collimation concluded that CT consistently underestimates the extent of
centrilobular and panlobular emphysema and the severity of emphysema
when compared with pathologic assessment (105,106,107,108). In spite of these limitations, CT is currently the best way to detect emphysema in living patients.
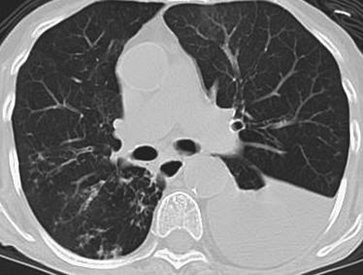 |
FIGURE 13-34. Infectious bronchiolitis. CT of a 72-year-old man with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
pneumonia shows tree-in-bud opacities in the right lower lobe and dense
airspace opacity and volume loss in the left lower lobe. |
The most common form of emphysema, centrilobular
emphysema, is strongly associated with cigarette smoking, with the
severity of emphysema increasing with the number of cigarettes smoked (109,110).
Centrilobular emphysema results from destruction of alveoli around the
proximal respiratory bronchiole and characteristically has a
predominantly upper lung distribution. Although the upper lungs are
more severely affected by emphysema, the degree of emphysema in the
lower lungs has a stronger correlation with pulmonary function
abnormalities. This indicates that the upper lungs are physiologically
a relatively silent region, where extensive destruction may occur
before functional abnormalities become detectable (111).
Panlobular emphysema has a characteristic lower
lobe–predominant distribution; this is the type of emphysema seen in
patients with α-1-antitrypsin deficiency (Fig. 13-37). In panlobular emphysema, the alveoli are destroyed throughout the secondary pulmonary lobule. The same findings of basilar
emphysema can be seen in patients who intravenously inject methylphenidate (crushed Ritalin tablets) (Fig. 13-38) (112).
P.232
P.233
emphysema can be seen in patients who intravenously inject methylphenidate (crushed Ritalin tablets) (Fig. 13-38) (112).
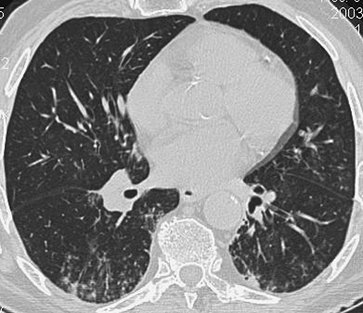 |
FIGURE 13-35. Aspiration. CT of a 77-year-old man with recurrent aspiration shows bronchiectasis and tree-in-bud opacities in both lower lobes. |
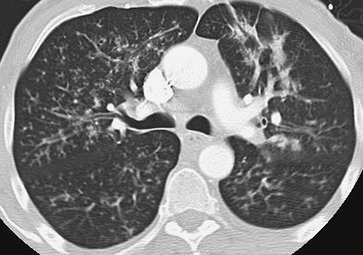 |
FIGURE 13-36. Aspiration. CT of a 57-year-old man with Parkinson disease and recurrent aspiration shows diffuse tree-in-bud opacities. |
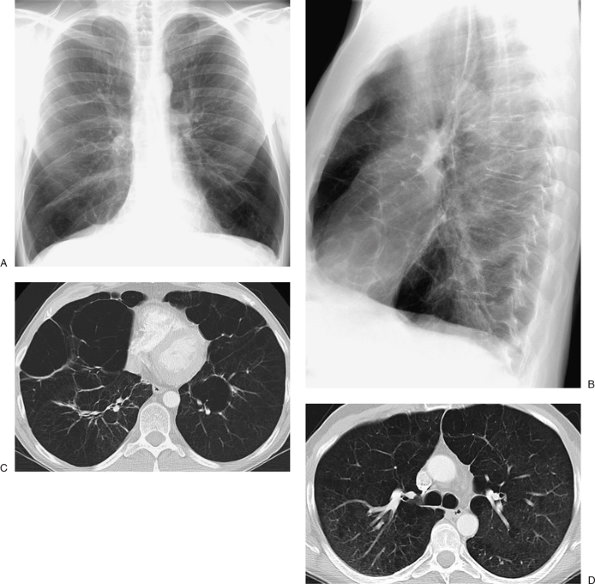 |
FIGURE 13-37. Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency. A: PA chest radiograph of a 43-year-old man shows hyperinflation and hyperlucency in the lower lungs. B: Lateral view shows increased retrosternal lucency and flattening of the diaphragm. C: CT shows bullous emphysema in the lower lungs. D:
CT at a more superior level shows less severe emphysema. Compared with
smoking-related centrilobular emphysema, emphysema caused by α-1-antitrypsin deficiency, although diffuse, is more severe in the lower lungs. |
TABLE 13-6 FEATURES OF THREE MORPHOLOGIC SUBTYPES OF EMPHYSEMA | ||
|---|---|---|
|
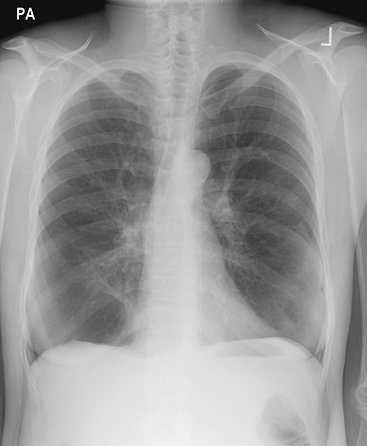 |
FIGURE 13-38. Methylphenidate (Ritalin) lung.
PA chest radiograph of a woman who intravenously injected crushed
Ritalin tablets shows emphysema in the lower lungs, which is similar in
appearance to the findings of α-1-antitrypsin deficiency. |
Paraseptal emphysema is a focal or multifocal
abnormality involving the periphery of the pulmonary lobule that is
almost always seen in the periphery of the lung along the fissures and
at sharp pleural reflections. Coalescence of paraseptal emphysema leads
to the formation of bullae and is important in the development of
spontaneous pneumothorax (113,114). Paraseptal emphysema should not be confused with honeycombing, which has thicker walls and is associated with fibrosis (115).
Criteria for chest radiographic diagnosis of emphysema include two or more of the following:
- Depression and flattening of the diaphragm on the posteroanterior (PA) chest radiograph and blunting of costophrenic angles, with the actual level of the diaphragm not as significant as the contour (this can be determined from a straight line connecting the costophrenic junction to the vertebrophrenic junction on each side; if the highest level of the diaphragm contour is less than 1.5 cm above this line, the diaphragm can be recorded as flat).
- Irregular radiolucency of the lung, as a result of irregularity in distribution of the emphysematous tissue destruction.
- Increased retrosternal radiolucency, as seen on the lateral view, measuring 2.5 cm or more from the sternum to the most anterior margin of the ascending aorta.
- Flattening or even concavity of the diaphragm contour on the lateral chest radiograph, as determined by the presence of a sternodiaphragmatic angle of 90 degrees or larger (100) (Fig. 13-39).
Other findings include increased AP diameter of the
chest, saber-sheath configuration of the trachea, narrow
cardiomediastinal silhouette, and enlargement of the central pulmonary
arteries and right ventricle when pulmonary artery hypertension and cor
pulmonale are present, respectively.
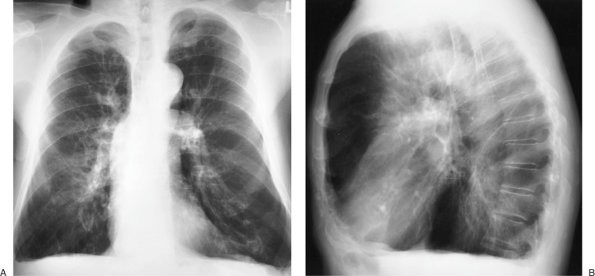 |
FIGURE 13-39. Emphysema. PA (A) and lateral (B)
chest radiographs of a long-time cigarette smoker show flattening of
the diaphragm with blunting of the costophrenic angles, increased
retrosternal lucency, increased AP diameter of the chest, and prominent
central pulmonary arteries. Note that the sternodiaphragmatic angle is
greater than 90 degrees, indicative of extreme flattening and even
minimal concavity of the diaphragmatic contour, as seen on the lateral
view. |
P.234
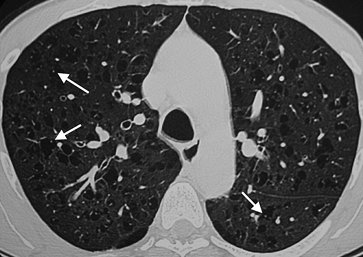 |
FIGURE 13-40. Centrilobular emphysema.
CT of a 50-year-old woman with a long history of cigarette smoking
shows focal areas of low attenuation creating a "Swiss cheese"
appearance. Note a central nodular opacity within several of the areas
of lucency (arrows); these opacities represent the lobular arteries. This finding helps to distinguish emphysema from cystic lung diseases. |
Thin-section CT shows centrilobular emphysema as focal
areas of low attenuation up to 1 cm in diameter within a homogeneous
background of lung parenchyma; occasionally, this results in a “Swiss
cheese” appearance. These areas of low attenuation are usually round or
oval, have no definable wall, and are often associated with a small
centrilobular "dot" representing the normal centrilobular core
structures (Fig. 13-40). The appearance of
panlobular emphysema on CT is large, extensive areas of uniform low
attenuation with a lower lobe–predominant distribution associated with
a reduction in the size and number of pulmonary vessels. No peripheral
preservation of the lobule occurs, and therefore no striking difference
in density exists between affected lobules and a homogeneous background
of normal pulmonary parenchyma. Because of this, mild to moderate
disease can be easily missed and the extent of disease underestimated (116). Paraseptal emphysema appears as multiple small subpleural airspaces ranging from a few millimeters to 1 cm in diameter (117).
Bullae, a term used synonymously with blebs, are
described as air-filled structures greater than 1 cm in diameter, with
thin walls, occurring in a subpleural or intraparenchymal location.
They are usually multiple or associated with paraseptal, centrilobular,
or panlobular emphysema (118). Giant bullous emphysema, or vanishing lung syndrome (Fig. 13-41), is
characterized by large bullae that are several centimeters in diameter and in some cases large enough to fill an entire hemithorax. When giant bullae impair pulmonary function and are associated with compressed lung on CT, the usual method of treatment is surgical resection (bullectomy) (119). On occasion, bullae can become infected and present as cystic masses with air–fluid levels (Figs. 13-42 and 13-43).
P.235
characterized by large bullae that are several centimeters in diameter and in some cases large enough to fill an entire hemithorax. When giant bullae impair pulmonary function and are associated with compressed lung on CT, the usual method of treatment is surgical resection (bullectomy) (119). On occasion, bullae can become infected and present as cystic masses with air–fluid levels (Figs. 13-42 and 13-43).
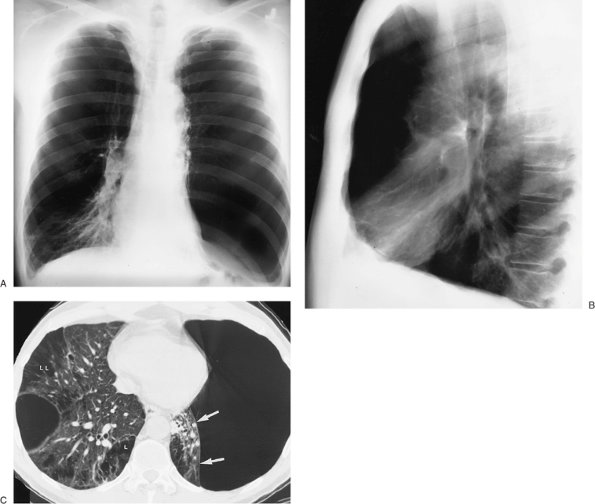 |
FIGURE 13-41. Giant bullous emphysema. PA (A) and lateral (B)
chest radiographs of a 47-year-old man with progressive severe
shortness of breath shows marked hyperinflation and hyperlucency of the
lungs. The vascular markings are sparse (so-called vanishing lung
sign), with the majority of residual perfusion going to the right
medial base. The crowding of vascular markings at the right lung base,
from compressive emphysema, should not be mistaken for focal pneumonia.
Pneumothorax can be confused with this appearance; in some cases, CT is
the only way to exclude a pneumothorax. C: CT shows a huge bulla in the left upper lobe that displaces the major fissure posteriorly and medially (arrows) and a prominent bulla in the right lower lobe. Note abnormal lucent emphysematous spaces within the lungs (L). |
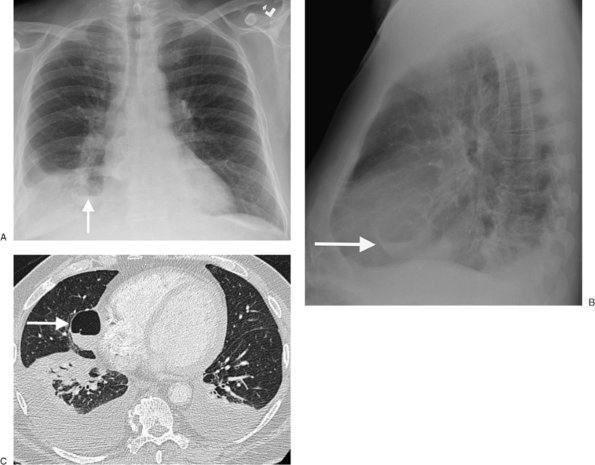 |
FIGURE 13-42. Infected bulla. A: PA chest radiograph of a 68-year-old man shows an air–fluid level in the right medial base (arrow). B: Lateral view shows a thin-walled cystic structure with an air–fluid level (arrow) in the right middle lobe. C: CT confirms a thin-walled bulla with an air–fluid level in the right middle lobe (arrow). Additional bullae were seen at several other levels on CT. |
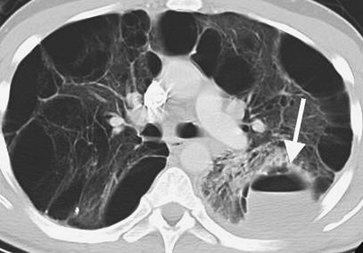 |
FIGURE 13-43. Infected bulla. CT of a 39-year-old man with α-1-antitrypsin deficiency shows a bulla with an air–fluid level (arrow) in the left lower lobe. |
References
1. Stern EJ, Graham CM, Webb WR, et al. Normal trachea during forced expiration: dynamic CT measurements. Radiology. 1993;187:27–31.
2. Breatnach E, Abbott GC, Fraser RG. Dimensions of the normal human trachea. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984; 141:903–6.
3. Brown BM, Oshita AK, Castellino RA. CT assessment of the adult extrathoracic trachea. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1983;7(3):415–418.
4. Gibellino F, Osmanliev DP, Watson A, et al. Increase in tracheal size with age - implications for maximal expiratory flow. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985;132:784–787.
5. Kwong JS, Adler BD, Padley SPG, et al. Diagnosis of diseases of the trachea and main bronchi: chest radiography vs CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1993;161:519–522.
6. Ferretti GR, Vining DJ, Knoplioch J, et al. Tracheobronchial tree: three-dimensional spiral CT with bronchoscopic perspective. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1996;20:777–781.
7. Kwong JS, Müller NL, Miller RR. Diseases of the trachea and main-stem bronchi: correlation of CT with pathologic findings. Radiographics. 1992;12:645–657.
8. Choplin RH, Wehunt WD, Theros EG. Diffuse lesions of the trachea. Semin Roentgenol. 1993;28:38–50.
9. Bateson EM, Woo-Ming M. Tracheobronchomegaly. Clin Radiol. 1973;24:354–358.
10. Woodring
JH, Howard RS II, Rehm SR. Congenital tracheobronchomegaly
(Mounier-Kuhn syndrome): a report of 10 cases and review of the
literature. J Thorac Imaging. 1991;6(2):1–10.
P.236
11. Dunne MG, Reiner B. CT features of tracheobronchomegaly. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1988;12:388–391.
12. Shin MS, Jackson RM, Ho KJ. Tracheobronchomegaly (Mounier-Kuhn syndrome): CT diagnosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988;150:777–779.
13. Fiser F, Tomanek A, Rimanova V, et al. Tracheobronchomegaly. Scand J Respir Dis. 1969;50:147–155.
14. Bhutani VK, Ritchie WG, Shaffer TH. Acquired tracheomegaly in very preterm neonates. Am J Dis Child. 1986;140:449–452.
15. Woodring JH, Barrett PA, Rehm SR, et al. Acquired tracheomegaly in adults as a complication of diffuse pulmonary fibrosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989;152:743–747.
16. Cavanaugh MJ, Cooper DM. Chronic pulmonary disease in a child with the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1976;65:679–684.
17. Wanderer
AA, Ellis EF, Goltz RW, et al. Tracheobronchiomegaly and acquired cutis
laxa in a child: physiologic and immunologic studies. Pediatrics. 1969;44:709–715.
18. Feist JH, Johnson TH, Wilson RJ. Acquired tracheomalacia: etiology and differential diagnosis. Chest. 1975;68:340–345.
19. Armstrong P, Wilson AG, Dee P, et al. Imaging of Diseases of the Chest. St. Louis: Mosby - Year Book; 1995:818.
20. Shepard JO, McLoud TC. Imaging the airways: computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Chest Med. 1991;12(1):151–168.
21. Stern EJ, Gamsu G. CT of the trachea and central bronchi. Radiologist. 1994;1(6):335.
22. Gamsu G, Webb WR. Computed tomography of the trachea and mainstem bronchi. Semin Roentgenol. 1983;18:51–60.
23. Grillo HC, Donahue DM, Mathisen DJ, et al. Postintubation tracheal stenosis: treatment and results. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1995;109:486–492.
24. Quint
LE, Whyte RI, Kazerooni EA, et al. Stenosis of the central airways:
evaluation by using helical CT with multiplanar reconstructions. Radiology. 1995;194:871–877.
25. Greene
R, Lechner GL. "Saber-sheath" trachea: a clinical and functional study
of marked coronal narrowing of the intrathoracic trachea. Radiology. 1975;115:265–268.
26. Greene R. "Saber-sheath" trachea: relation to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1978;130:441–445.
27. Fraser RG, Paré JAP, Paré PD, et al, eds. Diagnosis of Diseases of the Chest. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1990:1987–2003.
28. Davis SD, Berkmen YM, King T. Peripheral bronchial involvement in relapsing polychondritis: demonstration by thin-section CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989;153:953–954.
29. Müller NL, Miller RR, Ostrow DN, et al. Clinico-radiologic-pathologic conference: diffuse thickening of the tracheal wall. Can Assoc Radiol J. 1989;40:213–215.
30. Im J-G, Chung JW, Han SK. CT manifestations of tracheobronchial involvement in relapsing polychondritis. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1988;12: 792–793.
31. Lundgren R, Stjernberg NL. Tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica: a clinical bronchoscopic and spirometric study. Chest. 1981;80:706–709.
32. Secrest PG, Kendig TA, Beland AJ. Tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica. Am J Med. 1964;36:815–818.
33. Alroy GG, Lichtig C, Kaftori JK. Tracheobronchopathia osteoplastica: end stage of primary lung amyloidosis?. Chest. 1972;61:465–468.
34. Way SP. Tracheopathia osteoplastica. J Clin Pathol. 1967;20:814–820.
35. Young RH, Sandstrom RE, Mark GJ. Tracheopathia osteoplastica: clinical, radiologic, and pathological correlations. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1980;79:537–541.
36. Stein MG, Gamsu G, Webb WR, et al. Computed tomography of diffuse tracheal stenosis in Wegener granulomatosis. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1986;10:868–870.
37. Mendelson DS, Norton K, Cohen BA, et al. Bronchial compression: an unusual manifestation of sarcoidosis. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1983;7:892–894.
38. Westcott JL, Noehren TH. Bronchial stenosis in chronic sarcoidosis. Chest. 1973;63:893–897.
39. Coleman FP. Acquired non-malignant esophagorespiratory fistula. Am J Surg. 1957;93:321–328.
40. Spalding AR, Burney DP, Richie RE. Acquired benign bronchoesophageal fistulas in adults. Ann Thorac Surg. 1979;28:378–383.
41. Vaid YN, Shin MS. Computed tomography evaluation of tracheoesophageal fistula. J Comput Tomogr. 1986;10:281–285.
42. Carpenter LM, Merten DF. Radiographic manifestations of congenital anomalies affecting the airway. Radiol Clin North Am. 1991;29:219–240.
43. Wells
AL, Wells TR, Landing BH, et al. Short trachea, a hazard in tracheal
intubation of neonates and infants: syndromal associations. Anesthesiology. 1989;71:367–373.
44. McLaughlin FJ, Strieder DJ, Harris GBC, et al. Tracheal bronchus: association with respiratory morbidity in childhood. J Pediatr. 1985;106:751–755.
45. Shipley RT, McLoud TC, Dedrick CG, et al. Computed tomography of the tracheal bronchus. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1985;9(1):53–55.
46. Thurlbeck W. Pathology of chronic airflow obstruction. Chest. 1990; 97(suppl 2):6S–10S.
47. Grenier
P, Mourey-Gerosa I, Benali K, et al. Abnormalities of the airways and
lung parenchyma in asthmatics: CT observations in 50 patients and
inter- and intraobserver variability. Eur Radiol. 1996;6:199–206.
48. Neeld DA, Goodman LR, Gurney JW, et al. Computerized tomography in the evaluation of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990;142:1200–1205.
49. Paganin F, Trussard V, Seneterre E, et al. Chest radiography and high resolution computed tomography of the lungs in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992;146:1084–1087.
50. Carroll N, Elliot J, Morton A, et al. The structure of large and small airways in nonfatal and fatal asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993;147:405–410.
51. Stern EJ, Frank MS. Small airway diseases of the lungs: findings at expiratory CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994;163:37–41.
52. Kondoh
Y, Taniguchi H, Yokoyama S, et al. Emphysematous change in chronic
asthma in relation to cigarette smoking: assessment by computed
tomography. Chest. 1990;97:845–849.
53. Reid LM. Reduction in bronchial subdivision in bronchiectasis. Thorax. 1950;5:233–247.
54. Westcott JL, Cole SR. Traction bronchiectasis in end-stage pulmonary fibrosis. Radiology. 1986;161:665–669.
55. Gudbjerg CE. Roentgenologic diagnosis of bronchiectasis. An analysis of 112 cases. Acta Radiol. 1955;43:210–226.
56. Currie
DC, Cooke JC, Morgan AD, et al. Interpretation of bronchograms and
chest radiographs in patients with chronic sputum production. Thorax. 1987;42:278–284.
57. Silverman PM, Godwin JD. CT/bronchographic correlations in bronchiectasis. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1987;11(1):52–56.
58. Cooke JC, Currie DC, Morgan AD, et al. Role of computed tomography in diagnosis of bronchiectasis. Thorax. 1987;42:272–277.
59. Müller NL, Bergin CJ, Ostrow DN, et al. Role of computed tomography in the recognition of bronchiectasis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984;143:971–976.
60. Phillips MS, Williams MP, Flower CDR. How useful is computed tomography in the diagnosis and assessment of bronchiectasis? Clin Radiol. 1986;37:321–325.
61. Grenier P, Maurice F, Musset D, et al. Bronchiectasis: assessment by thin-section CT. Radiology. 1986;161:95–99.
62. Young K, Aspestrand F, Kolbenstvedt A. High resolution CT and bronchography in the assessment of bronchiectasis. Acta Radiol. 1991;32(6):439–441.
63. McGuinness G, Naidich DP, Leitman BS, et al. Bronchiectasis: CT evaluation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1993;160:253–259.
64. Afzelius BA. A human syndrome caused by immotile cilia. Science. 1976; 193:317–319.
65. Tsui LC, Buchwald M, Barker D, et al. Cystic fibrosis locus defined by a genetically linked polymorphic DNA marker. Science. 1985;230:1054–1057.
66. Kerem B, Rommens JM, Buchanan JA, et al. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: genetic analysis. Science. 1989;245:1073–1080.
67. Riordan
JR, Rommens JM, Kerem B, et al. Identification of the cystic fibrosis
gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989;245:1066–1073.
68. Rommens JM, Iannuzzi MC, Kerem B, et al. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: chromosome walking and jumping. Science. 1989;245:1059–1065.
69. Davis PB, Drumm M, Konstan MW. Cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996;154:1229–1256.
70. Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. Patient Registry 1994 Annual Data Report. Bethesda, MD: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation; 1995.
71. Fitzsimmons SC. The changing epidemiology of cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr. 1993;122:1–9.
72. Friedman
PJ, Harwood IR, Ellenbogen PH. Pulmonary cystic fibrosis in the adult:
early and late radiologic findings with pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981;136:1131–1144.
73. Bhalla M, Turcois N, Aponte V, et al. Cystic fibrosis: scoring system with thin-section CT. Radiology. 1991;179:783–788.
74. Fletcher
CM, Pride NB. Definitions of emphysema, chronic bronchitis, asthma, and
airflow obstruction: twenty-five years on from the CIBA Symposium. Thorax. 1984;39:81–85.
75. Kuhn C III. Normal anatomy and histology. In: Thurlbeck WM, Churg AM, eds. Pathology of the Lung. 2nd ed. New York: Thieme; 1995:1–36.
76. Murata
K, Itoh H, Todo G, et al. Centrilobular lesions of the lung:
demonstration by high-resolution CT and pathologic correlation. Radiology. 1986;161:641–645.
77. Stern EJ, Müller NL, Swensen SJ, et al. CT mosaic pattern of lung attenuation: etiologies and terminology. J Thorac Imaging. 1995;10:294–297.
78. Teel GS, Engeler CE, Tashijian JH, et al. Imaging of small airways disease. Radiographics. 1996;16:27–41.
79. Turton CW, Williams G, Green M. Cryptogenic obliterative bronchiolitis in adults. Thorax. 1981;36:805–810.
80. Padley
SPG, Adler BD, Hansell DM, et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans:
high-resolution CT findings and correlation with pulmonary function
tests. Clin Radiol. 1993;47:236–240.
81. Lynch DA, Brasch RC, Hardy KA, et al. Pediatric pulmonary disease: assessment with high-resolution ultrafast CT. Radiology. 1990;176:243–248.
82. Morrish
WF, Herman SJ, Weisbrod GL, et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans after lung
transplantation: findings at chest radiography and high-resolution CT. Radiology. 1991;179:487–490.
P.237
83. Sweatman MC, Millar AB, Strickland B, et al. Computed tomography in adult obliterative bronchiolitis. Clin Radiol. 1990;41:116–119.
84. Finkelstein R, Cosio M. Disease of the small airways in smokers: smokers' bronchiolitis. In: Epler G, ed. Diseases of the Bronchioles. New York: Raven Press; 1994:115–137.
85. Remy-Jardin
M, Remy J, Gosselin B, et al. Sliding thin slab, minimum intensity
projection technique in the diagnosis of emphysema: histopathologic - CT
correlation. Radiology. 1996;200:665–671.
86. Myers
JL, Veal CF, Shin MS, et al. Respiratory bronchiolitis causing
interstitial lung disease: a clinicopathologic study of six cases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987;135:880–884.
87. Wright JL, Cagle P, Churg A, et al. State of the art: diseases of the small airways. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992;146:240–262.
88. Gruden JF, Webb WR. CT findings in a proved case of respiratory bronchiolitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1993;161:44–46.
89. Remy-Jardin M, Remy J, Gosselin B, et al. Lung parenchymal changes secondary to cigarette smoking: pathologic - CT correlations. Radiology. 1993;186:643–651.
90. Akira M, Kitatani F, Yong-Sik L, et al. Diffuse panbronchiolitis: evaluation with high-resolution CT. Radiology. 1988;168:433–438.
91. Gruden
JF, Webb WR, Warnock M. Centrilobular opacities in the lung on HRCT:
diagnostic considerations and pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994;162:569–574.
92. Homma H, Yamanaka A, Tanimoto S, et al. Diffuse panbronchiolitis: a disease of the transitional zone of the lung. Chest. 1983;83:63–69.
93. Aquino SL, Gamsu G, Webb WR, et al. Tree-in-bud pattern: frequency and significance on thin section CT. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1996;20:594–599.
94. Collins J, Blankenbaker D, Stern EJ. CT patterns of bronchiolar disease: what is "tree-in-bud"? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998;171:365–370.
95. Snider GL. Distinguishing among asthma, chronic bronchitis, and emphysema. Chest. 1985;87:35S–39S.
96. Sobonya RE, Burrows B. The epidemiology of emphysema. Clin Chest Med. 1983;4:351–358.
97. Thurlbeck WM. Overview of the pathology of pulmonary emphysema in the human. Clin Chest Med. 1983;4:337–350.
98. Gelb AF, Gold WM, Wright RR, et al. Physiologic diagnosis of subclinical emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973;107:50–63.
99. Snider GL. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease - a continuing challenge. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986;133:942–944.
100. Pratt PC. Role of conventional chest radiography in diagnosis and exclusion of emphysema. Am J Med. 1987;82:998–1006.
101. Schmidt RA, Glenny RW, Godwin JD, et al. Panlobular emphysema in young intravenous Ritalin abusers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991;143:649–656.
102. Sherman CB, Hudson LD, Pierson DJ. Severe precocious emphysema in intravenous methylphenidate (Ritalin) abusers. Chest. 1987;92:1085–1087.
103. Kinsella
M, Müller NL, Abboud RT, et al. Quantitation of emphysema by computed
tomography using a "density mask" program and correlation with
pulmonary function tests. Chest. 1990;97:315–321.
104. Morrison
NJ, Abboud RT, Ramadan F, et al. Comparison of single breath carbon
monoxide diffusing capacity and pressure-volume curves in detecting
emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989;139:1179–1187.
105. Bergin C, Müller NL, Nochols DM, et al. The diagnosis of emphysema. A computed tomographic-pathologic correlation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986;133:541–546.
106. Foster WL Jr, Pratt PC, Roggli VL, et al. Centrilobular emphysema: CT-pathologic correlation. Radiology. 1986;159:27–32.
107. Hayhurst MD, Flenley DC, McLean A, et al. Diagnosis of pulmonary emphysema by computerized tomography. Lancet. 1984;2:320–322.
108. Miller RR, Müller NL, Vidal S, et al. Limitation of computed tomography in the assessment of emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989;139:980–983.
109. Auerbach O, Hammond EC, Garfinkel L, et al. Relationship of smoking and age to emphysema: whole-lung section study. N Engl J Med. 1972;286:853–857.
110. Niewoehner DE. Cigarette smoking, lung inflammation, and the development of emphysema. J Lab Clin Med. 1988;111:15–27.
111. Gurney
JW, Jones KK, Robbins RA, et al. Regional distribution of emphysema:
correlation of high-resolution CT with pulmonary function tests in
unselected smokers. Radiology. 1992;183:457–463.
112. Stern
EJ, Frank MS, Schmutz JF, et al. Panlobular pulmonary emphysema caused
by i.v. injection of methylphenidate (Ritalin): findings on chest
radiographs and CT scans. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994;162(3):550–560.
113. Anderson AE Jr, Furlaneto JA, Foraker AG. Bronchopulmonary derangements in non-smokers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1970;101:518–527.
114. Tuddenham
WJ. Glossary of terms for thoracic radiology: recommendations of the
Nomenclature Committee of the Fleischner Society. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984;143:509–517.
115. Stern
EJ, Frank MS. CT of the lung in patients with pulmonary emphysema:
diagnosis, quantification, and correlation with pathologic and
physiologic findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994;162:791–798.
116. Spouge D, Mayo JR, Cardoso W, et al. Panacinar emphysema: CT and pathologic findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1993;17(5):710–713.
117. Thurlbeck WM. Morphology of Emphysema and Emphysema-like Conditions. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1976:96–234.
118. Reid L. The Pathology of Emphysema. London: Lloyd-Duke (Medical Books); 1967.
119. Martinez
F. Surgical therapy for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease:
conventional bullectomy and lung volume reduction surgery in the
absence of giant bullae. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;20:351–364.